What is an oceanographic profile?#
Each of the temperature and salinity data sets measured from 2000 meters depth to surface is called an oceanographic profile, which is why the Argo floats are also known as “profilers”.
Usually in oceanography, observations are refered to the pressure level in decibar. The decibar is a multiple of the unit bar (bar) for pressure; the prefix deci (d) is a factor of one tenth or 0.1. Therefore, one decibar is 0.1 bars. The decibar is represented by the symbol dbar. The dbar is a metric unit of pressure defined as 10 kPa, though not part of the International System of Units (SI) is widely used in oceanography since you can get a rough idea of the depth in meters just looking the pressure in dbars and the rule of thumb than 1 meters is 1 dbar.
In the following video you will find a detailed explanation and some examples:
The Argo Online School 141 - The Argo Program. What is an oceanographic profile?
Therefore and argo float will measure Conductivity, Temperature, and Pressure, this is, a CTD profile, and from the CTD measurements we can obtain also the salinity. Here there is an Sketch of a profile:
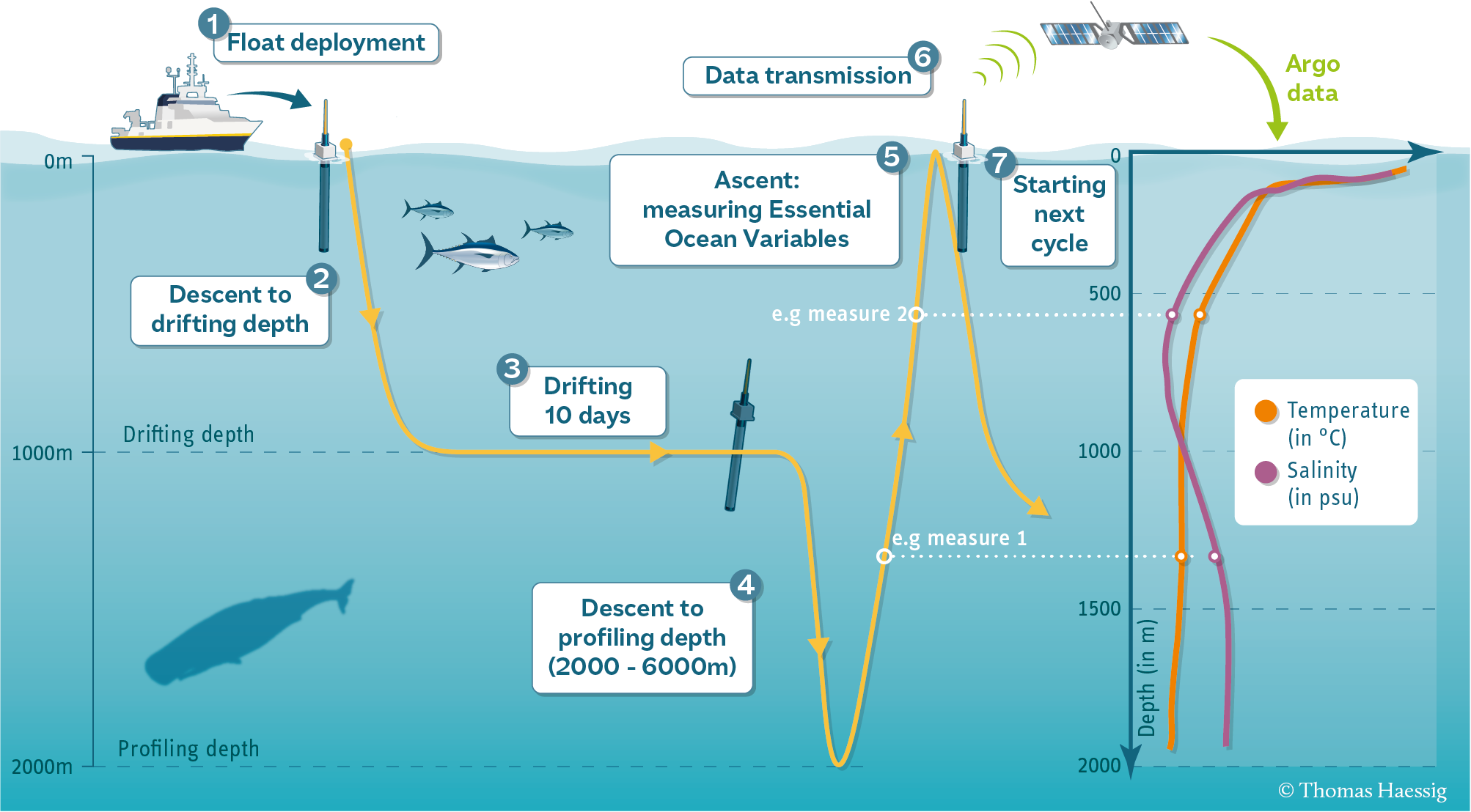
Usually in oceanography, the sensor that measures CTD it is also called a CTD.
Argo has been revolutionary#
Argo represents a revolution in ocean observation, since it provides data, freely and free of charge, at a rate 20 times higher compared to traditional methods on board oceanographic records. Here we present some more interesting facts:
The Argo Online School 142 - The Argo Program. What is an oceanographic profile?: Argo has been revolutionary
